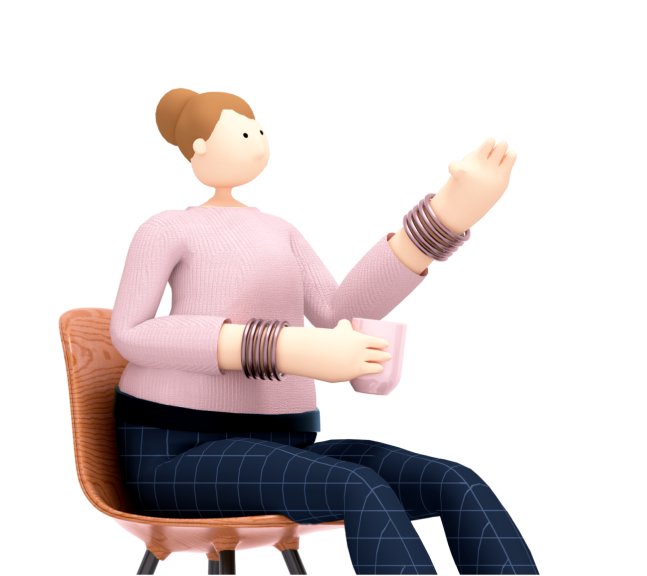
Why German Language?
The German language exam is a standardized test that assesses the proficiency level of individuals in the German language. There are several types of German language exams, each designed for different purposes and levels of proficiency.
The most common German language exams include:
Goethe-Institut exams: These exams are recognized worldwide and are suitable for those who want to study, work, or live in German-speaking countries. They assess your German language skills at various levels, from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced).
TestDaF: This exam is specifically designed for non-native speakers who want to enroll in a German-speaking university. It assesses your proficiency in reading, listening, writing, and speaking at levels B2 and C1.
To prepare for the German language exam, you can use various resources, such as textbooks, online courses, language exchange partners, or attending language schools. It's important to practice all four language skills and focus on improving your grammar and vocabulary.
Preparing for the German language exam can open up many opportunities for you, such as studying in a German-speaking country, working in Germany or other German-speaking countries, or simply improving your language skills for personal enrichment. Additionally, having a German language certificate can improve your chances of being selected for a job requiring German language skills or gaining admission to a German-speaking university.
Get a free consultation
Our specialized strategy
To score maximum score in your very first attempt.

Learn the basics of German grammar and vocabulary
Start with the basics of German grammar, including verb conjugation, noun gender, and sentence structure. Learn essential German vocabulary, such as common nouns, adjectives, and verbs. Use German textbooks, online courses, and language apps to reinforce your learning and practice your skills.

Listen to and watch authentic German media
Listen to German podcasts, music, and radio shows to improve your listening skills and familiarize yourself with German accents and intonation. Watch German movies, TV shows, and news programs to practice your listening and reading skills and learn about German culture. Use subtitles or transcripts to help you understand unfamiliar words and expressions.

Practice speaking and writing in German
Practice speaking German with native speakers, language exchange partners, or tutors to improve your pronunciation, fluency, and confidence. Write short essays, emails, or journal entries in German to improve your writing skills and expand your vocabulary. Use language exchange programs or online chat rooms to practice your communication skills and receive feedback on your language proficiency.

Take practice tests and track your progress
Take German language proficiency tests, such as the TestDaF or the Goethe-Institut exams, to evaluate your language proficiency and identify areas for improvement. Use practice tests, quizzes, and exercises to prepare for the exams and improve your language skills. Track your progress by setting goals and monitoring your performance over time, and adjust your study plan accordingly.
FAQs
Find answers to all your questions
German is a West Germanic language that is primarily spoken in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also widely spoken as a second language in many countries around the world.
No prerequisites are required for German Language, but some basic german proficiency and academic german knowledge is recommended. Preparation and practice tests are also recommended for the best possible score.
The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) has six levels of language proficiency, ranging from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced). Each level corresponds to a set of skills in reading, writing, listening, and speaking.
The most popular German language exams are the TestDaF, the Goethe-Institut exams (A1-C2), and the telc exams (A1-C2). These exams are designed to assess a candidate's proficiency in German and can be used for admission to universities, employment opportunities, or immigration purposes.
To prepare for a German language exam, it is important to develop your language skills in reading, writing, listening, and speaking. You can use textbooks, online courses, language apps, and language exchange programs to reinforce your learning. Additionally, taking practice tests and mock exams can help you evaluate your proficiency and identify areas for improvement.
The time it takes to learn German depends on your level of dedication, your learning style, and your language goals. However, it is generally estimated that it takes around 600-750 classroom hours of instruction to reach a B2 level of proficiency in German.
Many universities in Germany offer courses and programs in English, but it is still recommended to have some knowledge of German to fully immerse yourself in German culture and society. Additionally, some universities and programs may require a minimum level of German proficiency for admission.
The TestDaF (Test of German as a Foreign Language) is a language proficiency exam for non-native speakers of German. It measures a candidate's proficiency in reading, writing, listening, and speaking, and is commonly used for admission to universities in Germany.
The Goethe-Institut offers a range of language proficiency exams for non-native speakers of German. These exams are internationally recognized and can be used for admission to universities, employment opportunities, or immigration purposes.
The cost of a German language exam varies depending on the exam and the testing center. Generally, exam fees range from €80 to €300 or more. Some testing centers also offer preparation courses for an additional fee.
The time it takes to receive German language exam results varies depending on the exam and the testing center. Generally, you can expect to receive your results within a few weeks of taking the exam.
If you fail a German language exam, you can usually retake the exam after a certain period of time. It is important to review your exam results and identify areas where you need improvement in order to succeed in your retake. Some exams also offer preparation courses to help you improve your skills.
German language exam results are typically valid for a certain period of time, which varies depending on the exam and the purpose of the exam. For example, TestDaF exam results are valid for two years for university admission purposes, while Goethe-Institut exam results are valid for life. It is important to check the specific validity period of the exam you plan to take.
German language exam results are typically scored according to the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR), which has six levels of language proficiency ranging from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced). The exam results will indicate your proficiency level in each of the four language skills (reading, writing, listening, and speaking).